Unlike Linux, majority of tasks are performed by User Interface in Windows. But still, there are certain tasks that can be done through Command Prompt (CMD)
To most, the command prompt is a somewhat frightening frill of the Windows operating system. The interface is black, bleak, and without much assistance. Compared to the rest of the Windows interface, it just seems empty. Despite its underwhelming first impression, the command prompt is one of the most powerful instruments in the Windows arsenal.
The command prompt is useful for everything from complex automation to network configuration. What it lacks in interface it more than makes up for in effectiveness. If you don’t know where to start with command prompt proficiency, what better place than to start here!
CMD Commands
While most seek the best and most useful commands immediately, it helps to gloss over what different parameters mean. Proficiency with your command prompt comes not only through having a lexicon of commands, but of understanding what each parameter means and how different parameters can be combined to achieve a desired effect as well.
A–B
ASSOC - Displays or modifies file extension associations. ATTRIB - Displays or changes file attributes. BREAK - Sets or clears extended CTRL+C checking. BCDBOOT - Used to copy critical files to the system partition and to crate a new system BCD store. BCDEDIT - Sets properties in boot database to control boot loading.
C
CACLS - Shows or changes access control lists (ACLs) of files. CALL - Calls a batch program from another. CD - Shows the name of or changes to a current directory. CHCP - Displays or sets the active code page number. CHDIR - Displays the name of or changes to the current directory. CHKDSK - Checks a disk and displays a status report. CHKNTFS - Displays or modifies the checking of disk at boot time. CHOICE - Batch file command that allows users to select from a set of options. CIPHER - Displays or alters the encryption of directories (files) on NTFS partitions. CLIP - Redirects output off another command to the Windows clipboard. CLS - Clears the screen. CMD - Starts a new instance of the Windows command interpreter. CMDKEY - Creates, lists, and deletes stored user names and passwords or credentials. COLOR - Sets the default console colors. COMP - Compares the contents of two files or sets of files byte-by-byte. COMPACT - Displays or alters the compression of files on NTSF partitions. CONVERT - Converts FAT volumes to NTFS. You cannot convert the current drive. COPY - Copies one of more files to another location.
D
DATE - Displays or sets the date. DEFRAG - Disk defragment accessory. DEL - Deletes one or more files. DIR - Displays a list of files and sub-directories in a directory. DISKCOMP - Compares the contents of two floppy disks. DISKCOPY - Copies the contents of one floppy disk to another. DISKPART - Displays or configures Disk Partition properties. DOSKEY - Edits command lines, recalls Windows commands, and creates macros. DRIVERQUERY - Displays current device driver status and properties.
E
ECHO - Displays messages, or turns commands echoing on or off. ENDLOCAL - Ends localization of environment changes in a batch file. ERASE - Deletes one of more files. EXIT - Quits and closes the command shell. EXPAND - Expands compressed files.
F
FC - Compares two files or sets of files, and displays the differences between them. FIND - Searches for a text string in a file or files. FINDSTR - Searches for strings in files. FOR - Runs a specified command for each item in a set. FORFILES - Selects files in a folder for batch processing. FORMAT - Formats a disc for use with Windows. FSUTIL - Displays or configures the file system properties. FTYPE - Displays or modifies file types used in file extensions associations.
G–I
GOTO - Directs the Windows command interpreter to a labeled line in a batch program. GPRESULT - Displays Group Policy Information for machine or user. GRAFTABL - Enables Windows to display an extended character set in graphics mode. HELP - Provides help information for Windows commands. ICACLS - Display, modify, backup, or restore ACLs for files and directories. IF - Performs conditional processing in batch programs. IPCONFIG - Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values.
L–M
LABEL - Creates, changes, or deletes the volume label of a disk. MD - Creates a directory. MKDIR - Creates a directory. MKLINK - Creates Symbolic Links and Hard Links. MODE - Configures a system device. MORE - Displays output one screen at a time. MOVE - Moves one or more files from one directory to another directory.
O–P
OPENFILES - Queries, displays, or disconnects open files or files opened by network users. PATH - Displays or sets a search path for executable files. PAUSE - Suspends processing of a batch file. POPD - Restores the previous value of the current directory saved by PUSHD. PRINT - Prints a text file. PROMPT - Changes the Windows command prompt. PUSHD - Saves the current directory then changes it.
R
RD - Removes a directory. RECOVER - Recovers readable information from a bad or defective disk. REM - Designates comments (remarks) in batch files. REN - Renames a file or files. RENAME - Renames a file or files. REPLACE - Replaces files. RMDIR - Removes a directory. ROBOCOPY - Advanced utility to copy files and directory trees.
S
SET - Displays, sets, or removes environment variables for current session. SETLOCAL - Begins localization of environment changes in a batch file. SETX - Sets environment variables. SC - Displays or configures services (background processes). SCHTASKS - Schedules commands and programs to run on a computer. SHIFT - Shifts the position of replaceable parameters in batch files. SHUTDOWN - Allows proper local or remote shutdown of machine. SORT - Sorts input. START - Starts a separate window to run a specified programs or command. SUBST - Associates a path with a drive letter. SYSTEMINFO - Displays machine specific properties and configuration.
T
TAKEOWN - Allows an administrator to take ownership of a file. TASKLIST - Displays all currently running tasks including services. TASKKILL - Kill running process or applications. TIME - Displays or sets the system time. TIMEOUT - Pauses the command processor for the specified number of seconds. TITLE - Sets the window title for a CMD.EXE session. TREE - Graphically displays the directory structure of a drove or path. TYPE - Displays the contents of a text file.
V–X
VER - Displays the Windows version. VERIFY - Tells Windows whether or verify that your files are written correctly to a disk. VOL - Displays a disk volume label and serial number. VSSADMIN - Volume Shadow Copy Service administration tool. WHERE - Displays the locations of files that match a search pattern. WMIC - Displays WMI information inside interactive command shell. XCOPY - Copies files and directory trees.
Note: In order to have full access of the command prompt, you must run the prompt as an Administrator. Administrator privilege allows users to access commands otherwise inaccessible.
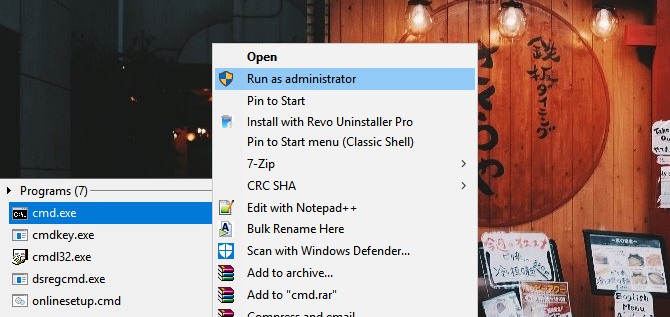
To activate Administrator mode, open your Start menu, type in cmd, right-click on the CMD program, and select Run as administrator. In Windows 10, you can also right-click the Start button and select Command Prompt (Admin).
Essential Command List
CMD commands number in the thousands, each one with its own action.
[command] /?
The above command provides users more information given particular commands. This tops the list, solely because it allows users the ability to figure out commands without having to rely on third party sources.Advertisement
Advertisement
chkdsk
Repairs file system errors, bad sectors, and recovers readable information. There are two methods of running the chkdsk command.
- chkdsk /F — Runs chkdsk and fixes file system errors.
- chkdsk /R — Fixes errors, locates bad sectors, and recovers information from those bad errors. A more comprehensive scan than /F.
ping, pathping, tracert
Ping and pathping (a more comprehensive form of ping) will echo or display data packets sent to and from a specific website. Pathping, along with tracert, will display the IP address of every router (or hop) on the way to your desired domain.
Advertisement
powercfg
By default, certain power configurations like Hibernation mode are off by default. Hibernation mode, as opposed to powering the PC off, will save the last state of your PC (programs, windows, etc.) and start up quicker. In order to enable or disable, use the following commands:
- powercfg /hibernate on — Turns on Hibernate mode, accessible through the default Windows power options.
- powercfg /hibernate off — Turns off Hibernate mode.
driverquery … > [File Name]
While most of us can’t make heads and tails of our PC drivers, there are times when driver issues will spring up. This may be as minor as a delay in performance, or as major as constant BSODs.
While the driverquery doesn’t present an immediate advantage, it does give an overview of the PC’s driver information in order to fully troubleshoot hardware and software issues.
- driverquery — Presents an assorted list of installed drivers.
- driverquery /FO TABLE, LIST or CSV — Presents your drivers as a Table, List, or excel spreadsheet.
If you add > [FileName.csv] to your original parameter — driverquery /FO CSV > driverquery.csv for example — your command prompt will take the information presented through driverquery and output it to an Excel sheet. The file will be directed to your Windows32 folder by default.
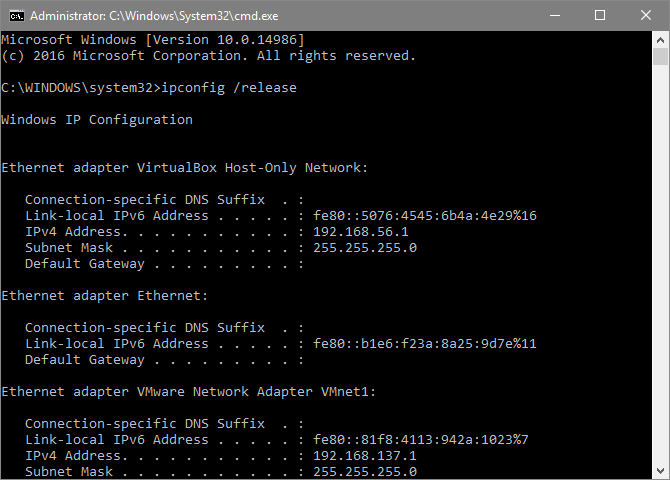
ipconfig /release, renew, flushdns
At times, network issues can occur through faulty IP addresses or corrupted DNS (Domain Name Server) files. To fix this, enter the following commands in order:
- ipconfig /release — Releases your IP address.
- ipconfig /renew — Replaces your previous IP address (and takes considerably longer to finish than the other two).
- ipconfig /flushdns — Erases the previously configured DNS listing, allowing websites that were previously unusable to load again.
It’s best only to do this when you’re having a network issue. More specifically, when you’re connected to the internet but certain websites won’t work.
Command Your Prompt!
The command prompt isn’t some strange beast made out to confuse you. It’s a simple feature, jam-packed with useful tools to control pretty much every aspect of your PC. We’ve only scratched the surface of what the command prompt has in store for you, so get to learning!